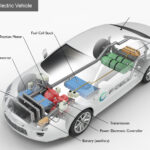
Catalytic conversion is a process in which molecules react with one another, but the reaction rate is increased by adding a catalyst. A catalyst is an element or compound that helps to speed up a chemical reaction without being consumed itself. This type of conversion occurs when fuel and air are mixed together and ignited, resulting in combustion.
The catalysts help to break down the molecules of fuel into smaller particles so they can mix more effectively with oxygen from the air for faster burning and more complete combustion. Catalytic converters also help reduce exhaust emissions by changing harmful gases such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, sulfur dioxide, and other particulate matter into less harmful compounds before releasing them out of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
Catalytic conversion is a chemical process that uses catalysts to convert hazardous pollutants in exhaust gases into less harmful substances. This process is commonly used by car manufacturers to reduce air pollution and make vehicles more environmentally friendly. Catalytic converters work by breaking down carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants into harmless compounds such as oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor and carbon dioxide.
This helps decrease the amount of smog-causing emissions that are released into the atmosphere from cars and trucks.
What Are Catalytic Converters | Environment | Chemistry | FuseSchool
What is Catalytic Conversion Process?
Catalytic conversion is a process used to convert organic compounds into simpler molecules. It involves the use of a catalyst, which acts as an agent to facilitate the chemical reaction between two or more substances without being consumed in the process. The catalytic converter uses this same concept but on a much larger scale, converting harmful pollutants from exhaust gases into less hazardous ones before they are released into the atmosphere.
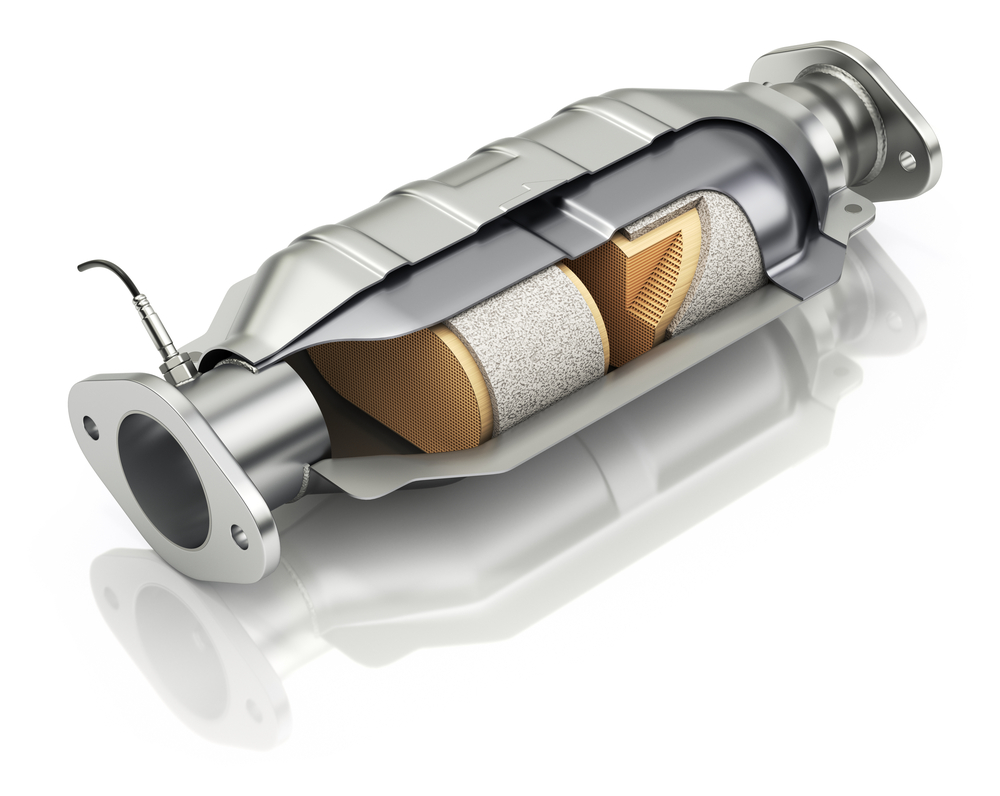
In catalytic converters, automobile exhaust gas containing nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC) is treated over a bed of ceramic honeycomb structures coated with precious metal such as platinum and palladium that act as catalysts. When these metals react with oxygen and other elements in the exhaust, they create stable compounds such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), and nitrogen gas (N2). Since each pollutant has its own type of oxidation reaction when exposed to different levels of heat along with certain concentrations of oxygen, different types of catalysts can be used for specific reactions.
This helps minimize emissions by providing optimal conditions for particular reactions to occur efficiently within the converter’s limited space; it also reduces backpressure on engines due to excess exhaust flow created by unburned fuel particles passing through them.
The whole system works together like a mini power plant: incoming air is mixed with fuel vaporized inside cylinders then burned within combustion chambers; hot gases produced from this burn are expelled out through valves where they pass over beds filled with catalyst materials; during their travel smaller molecular fragments form which escape via tailpipe producing fewer toxic pollutants than those present originally; finally clean air exits out at last completing cycle of catalysis/conversion process.
What is a Catalystic Converter?
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that reduces toxic gases and pollutants in automobile exhaust gas. It converts the poisonous carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) found in a car’s exhaust into less-harmful substances such as water vapor, nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. This process occurs when the chemical reactions take place on the surface of a special catalyst material which is usually made of metal or ceramic.
The catalytic converter plays an important role in controlling air pollution by reducing harmful emissions from cars and trucks.
The first catalytic converters were introduced in 1975 to comply with US federal regulations concerning vehicle emissions. Since then they have become standard equipment on all cars sold in North America and Europe as well as other countries around the world where environmental legislation exists to reduce vehicle emissions.
Catalytic converters are also widely used for industrial applications such as boilers and furnaces where they help reduce hazardous air pollutant levels by trapping noxious gases before they can be released into the atmosphere.
Catalytic converters work best when temperatures within their chamber reach 450 degrees Celsius (842 Fahrenheit).
Why Do People Want Catalytic Converters?
Catalytic converters are an important part of a vehicle’s emissions control system. They serve to reduce harmful exhaust gases from the vehicles, such as nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. By using these catalysts, toxic pollutants can be converted into harmless compounds before they escape into the atmosphere.
This helps protect our environment and ultimately contributes to human health by reducing air pollution.
The widespread use of cars has made it necessary for society to take steps towards cleaner air with less vehicular pollution. Catalytic converters help meet this goal by allowing engines to run more efficiently while also producing fewer dangerous pollutants in the process.
The main goal is that these devices will reduce fuel consumption and improve overall engine performance while simultaneously eliminating hazardous emissions which may contribute to global warming or acid rain problems.
In addition, many countries have adopted regulations requiring all new automobiles sold in their country must contain a catalytic converter in order for them to pass inspection and receive registration plates (or tags). Many governments understand that collective action is needed if we are going to make any real progress towards cleaner air quality; thus they require all drivers on public roads within their jurisdiction install a device like a catalytic converter so that everyone can benefit from its emission-reducing benefits collectively rather than individuals having no incentive or motivation on their own accord due this type of change out of personal interest alone being too costly for most people financially speaking when considering additional costs associated with installation/repairing replacement parts etc..
How Much is a Catalytic Conversion?
Catalytic conversion is an automotive process that converts harmful pollutants in exhaust gases into less harmful substances. It is a key part of the emissions control system found on most vehicles today, and its effectiveness has been proven time and again by stringent government testing standards.
The cost of catalytic converters varies depending on the type and size of vehicle, as well as the make and model year.
Generally speaking, aftermarket catalytic converter costs range from $100 to around $2,000 for newer models with complex systems; however, some specialty parts can cost even more than this. The easiest way to determine how much your specific catalytic converter will cost is to consult online fitment guides or contact your local auto parts store directly for a quote.
In addition to purchasing just the unit itself, many people opt for installation services as well; these typically run between $50-$200 depending on the complexity of the job and where you take it (dealership vs independent shop).
It’s also important to consider any additional labor charges that may be associated with replacing certain components such as oxygen sensors or other emission-related hardware before deciding whether or not a DIY approach would be beneficial in terms of financial savings versus potential damage caused by inexperience.
Finally, keep in mind that aside from direct costs related to purchase/installation there are other indirect expenses associated with catalytic converters such as fuel efficiency decreases due to clogged particulates which can lead higher operational costs over time if not addressed quickly enough – so it’s always best practice when dealing with any repairs/maintenance involving emissions equipment!

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Why are Catalytic Converters Stolen
Catalytic converters are frequently stolen because of their precious metals content. These parts contain palladium, platinum, and rhodium which can be sold for a high price on the black market. They are relatively easy to steal as they are only held in place by a few bolts and can be removed quickly with basic tools.
This makes them an attractive target for thieves looking to make quick money from scrap metal sales.
Catalytic Converter Problems
Catalytic converters are an important part of the exhaust system in a vehicle, as they help to reduce harmful emissions and pollutants. Unfortunately, catalytic converter problems can arise due to issues with their design or internal components. Common warning signs of a faulty catalytic converter include reduced engine performance, unusual noises from the exhaust system and increased fuel consumption.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to have your vehicle checked out by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible in order to avoid further damage.
How Does a Catalytic Converter Work
A catalytic converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s emissions control system. It works by converting harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases into less harmful ones before they are released into the atmosphere. The converter contains a combination of metals and chemicals, often platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which act as catalysts to break down pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor.
This helps reduce air pollution that can cause respiratory health issues for humans and other living organisms.
Conclusion
Catalytic conversion is a process used to convert waste into useful products. This method has many advantages, including its ability to reduce the amount of waste produced and its ability to be applied in different sectors such as industry, agriculture, and energy production. It can also help reduce air pollution by reducing the emission of pollutants.
In conclusion, catalytic conversion is an important tool that can be used to create more efficient and environmentally friendly products from our growing amounts of waste materials.